Micrometer AppOptics
AppOptics is a dimensional time-series SaaS with built-in dashboarding.
1. Installing micrometer-registry-appoptics
It is recommended to use the BOM provided by Micrometer (or your framework if any), you can see how to configure it here. The examples below assume you are using a BOM.
1.1. Gradle
After the BOM is configured, add the following dependency:
implementation 'io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-appoptics'| The version is not needed for this dependency since it is defined by the BOM. |
1.2. Maven
After the BOM is configured, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-appoptics</artifactId>
</dependency>| The version is not needed for this dependency since it is defined by the BOM. |
2. Configuring
The following example configures an AppOptics instance:
AppOpticsConfig appopticsConfig = new AppOpticsConfig() {
@Override
public String apiToken() {
return MY_TOKEN;
}
@Override
public @Nullable String get(String k) {
return null;
}
};
MeterRegistry registry = new AppOpticsMeterRegistry(appopticsConfig, Clock.SYSTEM);AppOpticsConfig is an interface with a set of default methods. If, in the implementation of get(String k), rather than returning null, you instead bind it to a property source, you can override the default configuration. For example, Micrometer’s Spring Boot support binds properties that are prefixed with management.metrics.export.appoptics directly to the AppOpticsConfig:
management.metrics.export.appoptics:
api-token: YOURKEY
# You will probably want disable AppOptics publishing in a local development profile.
enabled: true
# The interval at which metrics are sent to AppOptics. The default is 1 minute.
step: 1m3. Graphing
This section serves as a quick start to rendering useful representations in AppOptics for metrics that originate in Micrometer.
3.1. Timers
The AppOptics implementation of Timer produces three fields in AppOptics:
-
count: Rate of number of calls/second. -
sum: Rate of total time/second. -
max: A sliding window showing the maximum amount recorded.
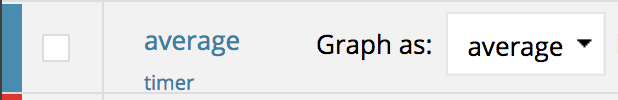
AppOptics performs the sum/count division dimensionally to generate aggregable averages on your behalf.