|
For the latest stable version, please use Micrometer 1.16.3! |
Micrometer AppOptics
AppOptics is a dimensional time-series SaaS with built-in dashboarding.
1. Installing
For Gradle, add the following implementation:
implementation 'io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-appoptics:latest.release'For Maven, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-appoptics</artifactId>
<version>${micrometer.version}</version>
</dependency>2. Configuring
The following example configures an AppOptics instance:
AppOpticsConfig appopticsConfig = new AppOpticsConfig() {
@Override
public String apiToken() {
return MY_TOKEN;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String get(String k) {
return null;
}
};
MeterRegistry registry = new AppOpticsMeterRegistry(appopticsConfig, Clock.SYSTEM);AppOpticsConfig is an interface with a set of default methods. If, in the implementation of get(String k), rather than returning null, you instead bind it to a property source, you can override the default configuration. For example, Micrometer’s Spring Boot support binds properties that are prefixed with management.metrics.export.appoptics directly to the AppOpticsConfig:
management.metrics.export.appoptics:
api-token: YOURKEY
# You will probably want disable AppOptics publishing in a local development profile.
enabled: true
# The interval at which metrics are sent to AppOptics. The default is 1 minute.
step: 1m3. Graphing
This section serves as a quick start to rendering useful representations in AppOptics for metrics that originate in Micrometer.
3.1. Timers
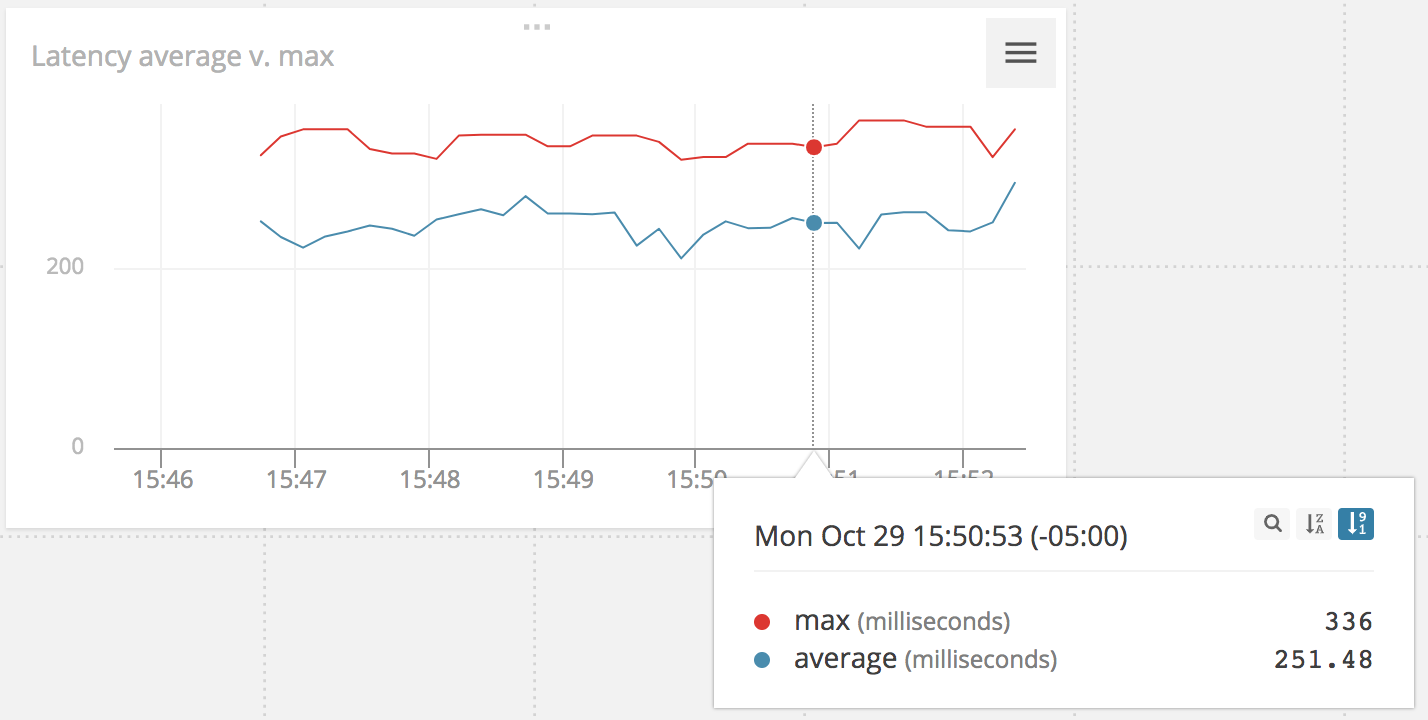
The AppOptics implementation of Timer produces three fields in AppOptics:
-
count: Rate of number of calls/second. -
sum: Rate of total time/second. -
max: A sliding window showing the maximum amount recorded.
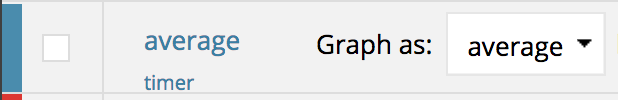
AppOptics performs the sum/count division dimensionally to generate aggregable averages on your behalf.