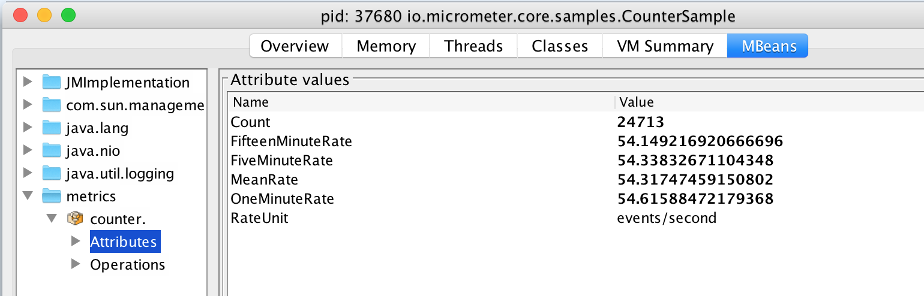
|
For the latest stable version, please use Micrometer 1.16.3! |
Micrometer JMX
Micrometer provides a hierarchical mapping to JMX, primarily as a cheap and portable way to view metrics locally. Where JMX exporting is found in production, the same metrics are generally exported to another, more purpose-fit monitoring system.
1. Installing micrometer-registry-jmx
It is recommended to use the BOM provided by Micrometer (or your framework if any), you can see how to configure it here. The examples below assume you are using a BOM.
1.1. Gradle
After the BOM is configured, add the following dependency:
implementation 'io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-jmx'| The version is not needed for this dependency since it is defined by the BOM. |
1.2. Maven
After the BOM is configured, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-jmx</artifactId>
</dependency>| The version is not needed for this dependency since it is defined by the BOM. |
Micrometer also sometimes scrapes data from JMX beans for use in reporting metrics. This registry implementation is not needed for these uses. Rather, this module is strictly used to export data to JMX.
2. Hierarchical name mapping
Micrometer provides a HierarchicalNameMapper interface that governs how a dimensional meter ID is mapped to flat hierarchical names.
The default (HierarchicalNameMapper.DEFAULT) sorts tags alphabetically by key and appends tag key/value pairs to the base meter name with '.' — for example, http_server_requests.method.GET.response.200. The name and tag keys have the registry’s naming convention applied to them first.
If there is something special about your naming scheme that you need to honor, you can provide your own HierarchicalNameMapper implementation. The most common cause of a custom mapper comes from a need to prefix something to the front of every metric (generally something like app.<name>.http_server_requests.method.GET.response.200).